Niacinamide, also known as Vitamin B3 or nicotinamide, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. It is an essential nutrient, meaning the body cannot produce it on its own and must obtain it through diet or supplements. Niacinamide has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits and its role in skincare. In this comprehensive essay, we will delve into the various aspects of niacinamide, including its functions, sources, benefits, potential side effects, and its use in skincare.
Everything You Should Know About Niacinamide

1. Functions of Niacinamide:
Niacinamide serves as a vital component in several enzymatic reactions, influencing a wide range of cellular functions. Some of the key functions of niacinamide include:
i. Energy Metabolism:
Niacinamide plays a critical role in energy production, as it is a precursor for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). These coenzymes are essential for converting nutrients into energy through various metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
ii. Cellular Repair and DNA Synthesis:
Niacinamide is involved in DNA repair and synthesis processes, helping maintain the integrity of the cell’s genetic material. It supports the production and repair of DNA, ensuring proper cellular functioning and growth.
iii. Antioxidant Activity:
As a precursor to NADPH, niacinamide aids in the generation of reduced glutathione, an essential antioxidant within cells. This helps neutralize harmful free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative stress and damage.
iv. Cellular Communication:
Niacinamide has been implicated in cell signaling pathways, affecting gene expression and cellular communication. It influences various cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis.
2. Sources of Niacinamide:
Niacinamide can be obtained from various dietary sources, and the body can also synthesize it from the essential amino acid tryptophan. Some common dietary sources of niacinamide include:
- Meat (poultry, beef, pork)
- Fish (tuna, salmon)
- Nuts and seeds (peanuts, sunflower seeds)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
- Whole grains (brown rice, barley)
- Dairy products (milk, yogurt)
In addition to dietary sources, niacinamide can be taken as a supplement in various forms, such as capsules or tablets.

3. Health Benefits of Niacinamide:
Niacinamide offers several health benefits due to its involvement in critical physiological processes. Some of the potential benefits of niacinamide are as follows:
i. Cardiovascular Health:
Niacinamide has been shown to support cardiovascular health by positively affecting lipid profiles. It helps reduce levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing “good” HDL cholesterol levels, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
ii. Skin Health:
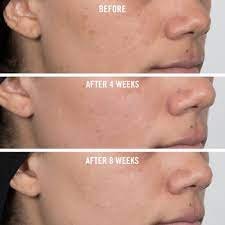
Niacinamide’s benefits extend to skincare as well. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it effective in treating various skin conditions. Niacinamide has been found to help improve the skin barrier function, reduce hyperpigmentation, and manage acne-prone skin. It also helps retain skin moisture, promoting a healthy complexion.
iii. Brain Function:
Niacinamide’s involvement in cellular communication and neural pathways suggests that it may play a role in supporting brain health and cognitive function. Studies have shown potential benefits in age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative conditions, although further research is needed in this area.
iv. Diabetes Management:
Niacinamide has been studied for its potential role in improving insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, making it a potential adjunct therapy for diabetes management. However, more research is needed to establish its effectiveness in this regard.
v. Immune System Support:
Niacinamide’s role in supporting cellular repair and DNA synthesis can indirectly benefit the immune system by promoting overall health and vitality.

4. Potential Side Effects and Precautions:
Niacinamide is generally well-tolerated when consumed within recommended daily intake levels. Excessive intake of niacinamide, particularly through supplements, can lead to adverse effects, such as flushing, itching, and gastrointestinal disturbances. These side effects are more commonly associated with niacin (nicotinic acid), another form of Vitamin B3.
Individuals with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications should exercise caution when supplementing with niacinamide. People with liver disease, kidney disease, or a history of gout should consult a healthcare professional before starting any niacinamide supplementation. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should also seek medical advice before using niacinamide supplements.

5. Niacinamide in Skincare:
In recent years, niacinamide has gained significant popularity in the skincare industry due to its numerous benefits for the skin. Some of the notable skincare benefits of niacinamide include:
i. Moisturization and Barrier Repair:
Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin barrier, reducing moisture loss and improving hydration. This leads to smoother, more supple skin.
ii. Reduction of Hyperpigmentation:
Niacinamide has been shown to reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation by inhibiting the transfer of melanin to the skin’s surface.
iii. Anti-Aging Properties:
As an antioxidant, niacinamide helps neutralize free radicals, preventing premature aging and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
iv. Acne Management:
Niacinamide’s anti-inflammatory properties make it effective in managing acne-prone skin. It helps reduce redness and inflammation associated with acne while regulating sebum production.
v. Minimization of Pore Size:
Regular use of niacinamide has been reported to help minimize the appearance of pores, giving the skin a smoother texture.
vi. Even Skin Tone:
Niacinamide’s ability to regulate melanin production contributes to a more even skin tone and improved complexion.
It is essential to note that individual skin types may respond differently to niacinamide, and potential interactions with other skincare ingredients should be considered. To incorporate niacinamide into a skincare routine, it is advisable to use products containing 2% to 5% niacinamide concentration. It is also recommended to perform a patch test before using new skincare products to check for any adverse reactions.
Niacinamide, also known as Vitamin B3 or nicotinamide, is an essential nutrient with a wide range of functions in the human body. From energy metabolism to skincare benefits, niacinamide plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Whether consumed through diet or utilized in skincare products, niacinamide’s versatility and potential benefits make it a valuable compound worthy of attention in various fields of health and wellness.
As with any dietary supplement or skincare ingredient, it is crucial to seek professional advice and follow recommended guidelines to ensure safe and effective use. The research on niacinamide’s benefits continues to evolve, and future studies will likely uncover even more fascinating aspects of this remarkable vitamin.

