Chlorella is a single-celled, freshwater microalgae that belongs to the phylum Chlorophyta. With a history dating back over two billion years, chlorella is one of the oldest known life forms on Earth. This green superfood has gained popularity in recent years due to its exceptional nutritional profile and potential health benefits. Chlorella is renowned for its ability to provide essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, proteins, and antioxidants, making it a promising dietary supplement and a potential solution to malnutrition. In this essay, we will delve into the origins, nutritional content, health benefits, potential uses, and environmental significance of chlorella.
Chlorella: An In-Depth Exploration of a Green Superfood
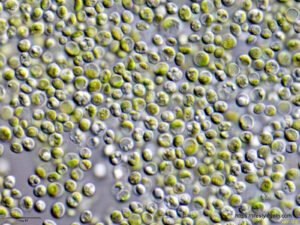
Section 1: The Origins and Properties of Chlorella
1.1 Historical Significance:
Chlorella’s history can be traced back to the early Earth, where it played a significant role in producing the oxygen-rich atmosphere we have today. The fossil record shows that chlorella was a crucial part of ancient marine ecosystems, contributing to the formation of limestone and other sedimentary rocks. Its ability to photosynthesize, converting carbon dioxide into oxygen, has made it a pivotal organism in the Earth’s history.
1.2 Microscopic Wonder:
Chlorella is a single-celled, spherical microorganism that measures about 2 to 10 micrometers in diameter. It thrives in freshwater environments, such as ponds and lakes, where it reproduces rapidly under the right conditions. Under a microscope, chlorella displays a green coloration due to the presence of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis.

Section 2: Nutritional Content of Chlorella
2.1 Proteins and Amino Acids:
Chlorella is an exceptional source of plant-based protein, containing all nine essential amino acids required for human health. Its protein content ranges from 50% to 60% of its dry weight, making it a valuable protein supplement for vegetarians, vegans, and individuals seeking alternative protein sources. Chlorella’s protein is highly digestible and contains essential amino acids, such as lysine, methionine, and cysteine.
2.2 Vitamins and Minerals:
Chlorella is a rich source of vitamins, including vitamin C, vitamin B complex (B1, B2, B3, B6, and B12), and vitamin E. Additionally, it contains various essential minerals, such as iron, calcium, magnesium, zinc, and potassium. These vitamins and minerals are essential for various physiological functions, including immune support, energy production, and bone health.
2.3 Antioxidants:
Chlorella is loaded with potent antioxidants, including beta-carotene, lutein, and chlorophyll. These antioxidants play a critical role in neutralizing free radicals, reducing oxidative stress, and protecting the body against cellular damage. The high concentration of chlorophyll in chlorella contributes to its detoxification properties and potential anti-cancer effects.
2.4 Dietary Fiber:
Chlorella contains significant amounts of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion, regulates bowel movements, and supports gut health. The fiber in chlorella may also help in weight management by promoting satiety and controlling appetite.

Section 3: Health Benefits of Chlorella
3.1 Immune System Support:
The presence of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in chlorella contributes to its immune-boosting properties. Research suggests that regular consumption of chlorella may enhance immune function, helping the body defend against infections and diseases.
3.2 Detoxification:
Chlorella is often hailed for its detoxification properties, attributed to its high chlorophyll content. Chlorophyll helps eliminate toxins, heavy metals, and harmful pollutants from the body. Some studies suggest that chlorella can aid in removing toxic substances like cadmium and lead from the liver and other tissues.
3.3 Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Chlorella’s anti-inflammatory properties have been explored in various studies. Chronic inflammation is linked to several chronic diseases, including arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. The antioxidants in chlorella may help reduce inflammation and alleviate related symptoms.
3.4 Cardiovascular Health:
Chlorella’s high content of antioxidants, such as beta-carotene and lutein, may support cardiovascular health by reducing oxidative stress and protecting against cholesterol oxidation. Chlorella’s potential to lower blood pressure and improve lipid profiles has been investigated in some studies, showing promising results.
3.5 Weight Management:
Chlorella’s rich protein and fiber content may aid in weight management. Protein helps in maintaining muscle mass, which is crucial for a healthy metabolism, while dietary fiber promotes satiety, reducing the overall caloric intake and preventing overeating.
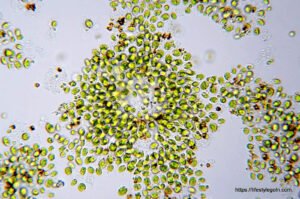
Section 4: Potential Uses of Chlorella
4.1 Nutritional Supplementation:
Chlorella is commonly used as a dietary supplement to provide essential nutrients and boost overall health. Its complete protein profile, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants make it an attractive option for individuals with dietary restrictions, athletes, and those seeking optimal nutrition.
4.2 Alternative Protein Source:
As the global demand for protein rises, chlorella presents a sustainable and nutrient-dense alternative to traditional protein sources. Its rapid growth and minimal environmental impact make it an eco-friendly solution to address protein shortages and food security challenges.
4.3 Cosmetic and Personal Care:
Chlorella’s detoxification properties and rich antioxidant content have found applications in the cosmetic and personal care industries. It is used in skincare products for its potential to promote healthy skin, reduce the signs of aging, and improve skin texture.
4.4 Water Treatment:
The ability of chlorella to absorb heavy metals and toxins from water has been explored in water treatment processes. Researchers have investigated using chlorella to purify polluted water bodies and remove contaminants, thus offering a sustainable solution for water treatment.
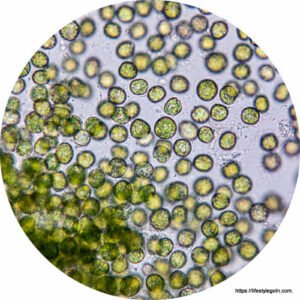
Section 5: Environmental Significance and Sustainability
5.1 Carbon Sequestration:
Chlorella’s photosynthetic activity enables it to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making it an important player in carbon sequestration. As part of a sustainable approach to combat climate change, chlorella cultivation may contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
5.2 Wastewater Treatment:
Chlorella has shown promise in treating wastewater and agricultural runoff. It can remove excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are significant contributors to water pollution. Implementing chlorella-based wastewater treatment systems may help mitigate environmental impacts and preserve water quality.
5.3 Bioremediation:
Chlorella has the potential to remediate polluted environments, including areas affected by heavy metals and organic contaminants. Its ability to absorb and accumulate pollutants makes it a valuable candidate for bioremediation applications.
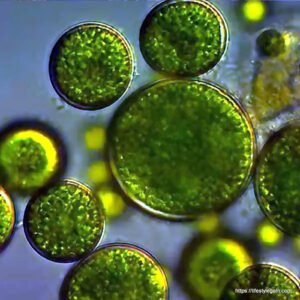
Section 6: Safety and Precautions
6.1 Heavy Metal Contamination:
Since chlorella has the capacity to absorb heavy metals from its environment, there is a concern that commercially available chlorella supplements might contain heavy metal contaminants. It is essential to source chlorella products from reputable suppliers who perform rigorous quality control tests to ensure safety.
6.2 Allergic Reactions:
Some individuals may be sensitive to chlorella and may experience allergic reactions, such as skin rashes, digestive discomfort, or respiratory issues. Anyone considering using chlorella as a dietary supplement should consult a healthcare professional, especially if they have known allergies to algae or other marine organisms.

Section 7: Future Directions and Research
7.1 Genomic Studies:
Advancements in genomic research may uncover the full potential of chlorella as a versatile and sustainable source of nutrition and bioactive compounds. Understanding the genetic makeup of chlorella may lead to the development of specialized strains with enhanced nutritional profiles or improved bioremediation capabilities.
7.2 Clinical Trials:
More extensive and well-controlled clinical trials are needed to fully validate the health benefits of chlorella. These trials can provide valuable insights into the specific mechanisms of action and the appropriate dosages required for various health conditions.
7.3 Algae Farming and Aquaculture:
Given chlorella’s rapid growth and high nutritional content, there is a need for further research on large-scale algae farming and aquaculture practices. Sustainable chlorella cultivation methods may revolutionize the food and supplement industries, offering environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional agricultural practices.

Chlorella is a remarkable microalgae with a rich history, exceptional nutritional content, and a wide range of potential health benefits. Its role as a green superfood and a sustainable solution to global nutrition and environmental challenges has garnered increasing interest from researchers, health enthusiasts, and environmentalists alike.
While further research is required to fully unlock the potential of chlorella, its widespread availability as a dietary supplement and its versatile applications in various industries make it a promising candidate for improving human health and addressing environmental concerns.
As we delve deeper into the wonders of chlorella, embracing its potential and incorporating it into our diets and sustainable practices can contribute to a healthier and more resilient planet for generations to come.

